October 4, 2021
Best Privacy Tools of January 2026: A Complete Guide
In the words of Edward Snowden in his memoir Permanent Record: “ Saying that you don't care about [...]

WHAT’S IN THIS REVIEW?
Disclaimer: Partnerships & affiliate links help us create better content. Learn how.
For anyone looking for tools to provide enhanced online anonymity, VPNs and the Tor browser are potential solutions that you may have already heard of.
In a nutshell, Tor (The Onion Router) is a cost-effective browser option released by a nonprofit organization, and a virtual private network (VPN) is a commercial solution that offers more flexibility. That’s a simple rundown for a topic that needs a more in-depth explanation in order to be understood properly.
This guide will take you through everything there is to know about VPNs and Tor. This includes pros and cons, main feature differences, and what to expect while using a combination of the duo.
As far as secure web browsers go, Tor is arguably the best solution for privacy-focused users. Tor (The Onion Router) is completely free to use and is run by a non-profit organization based in Massachusetts. It’s a browser that is used to prevent anyone from knowing about the websites you visit, by sending your web traffic through three random relays (or servers) contained in the network. There’s a total of roughly 7,000 of these relays, often provided by volunteers. The first two simply receive the traffic and pass it along. The last is an exit relay, so their IP address is seen as the source of any traffic.
As your traffic is being routed and rerouted through the network, not even Tor can tell where you’ve visited or what you’ve been up to. As such, it’s one of the safest ways to access the dark web. This can also lead to complaints, such as copyright takedown notices or issues if an exit node has been used inappropriately. (Of course, this will only affect the volunteer providing the exit node.)
They source funding from larger corporations, including the U.S. government, which was heavily involved during the 2010s. As recently as 2015, U.S. government sources; ‘accounted for 80-90 percent of its financial backing’, although that figure dropped to just over 50 percent by 2017. They have switched to a model of support thanks to users and smaller companies in the present, aiming to lessen their reliance on Uncle Sam.
The use of a layered approach is how Tor earned its name, while you’ll also be able to access onion sites that are only available via the browser. However, your ISP will still be able to see that you’re accessing Tor, even if they can’t see the final destination point.
We’ve listed some of the main pros associated with the use of Tor below:
Nothing in life is perfect, so here are the main cons associated with Tor
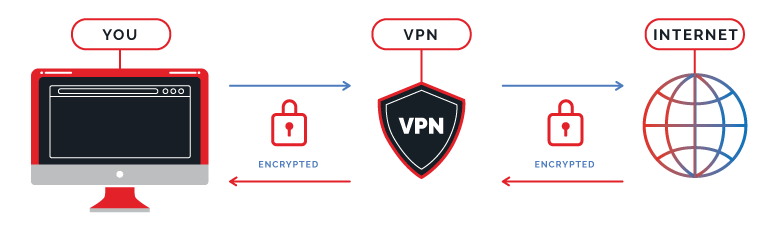
A VPN is used to send data to and from your device via an encrypted tunnel. This gives the user improved anonymity while keeping your data safe from the likes of your ISP or hackers. Both free and premium VPN options exist, although we’d strongly advocate for the use of the latter if privacy is your main aim. After all, free providers have been caught out in the past.
VPNs need to be trusted to get rid of any personal data collected on their servers, while many commit to a no-logs policy which means they keep nothing whatsoever. (We’d stick with an audited service to be sure.)
A VPN works by connecting the user to a server that is owned or rented by the provider. It can be found in many locations around the world. A VPN that works with Netflix will trick websites into thinking that the new IP address you’ve been assigned is real, which is how VPNs are used to unblock internationally blocked sites.
Here are some of the main benefits you’ll find while using a VPN:
VPNs also have a number of cons to consider:
The differences may be more subtle than you might have expected. However, we’d almost always opt for the use of a VPN instead of Tor for improved online security.
Of course, this depends on the service you’ve selected. I’d rather suffer from slower speeds and a service I can trust with the Tor browser, as opposed to a free VPN which might be leaking or giving away my data in the meantime.
Remember, if you need to connect to a .onion site, a VPN will be useless without the Tor browser.
If you’re thinking about using either Tor, a secure VPN, or a combination of the two, we’ve listed a trio of providers which will have you covered.
NordVPN is great if you’re looking for an alternative to Tor as it can be used to bypass geographical restrictions easily. They have over 5200+ servers in 60 countries, and the app automatically chooses the fastest server in a selected country. Another solid security feature is found in the form of their WireGuard-based protocol called NordLynx.
As a twice audited no-logs service, it ticks all of the boxes.
If you’re looking for a large list of server locations and dedicated streaming support, CyberGhost has you covered. They allow for up to seven simultaneous connections. Not to mention, additional security features include ad and malware blocking and automatic redirection to the most secure version of any website you visit.
Private Internet Access (PIA) is one of the most secure and affordable VPNs on the market. You can protect up to 10 devices at once with a single PIA subscription for under $3 per month. With it, you’ll receive military-grade AES 256-bit encryption and multiple protocols such as IKEv2, IPSec, and OpenVPN (TCP/UDP).
Rather than lining up a VPN vs Tor, the combined power of a VPN and Tor is another method to increase online privacy and security. However, it’s not necessarily a good idea, as Tor notes:
‘A VPN/SSH acts either as a permanent entry or as a permanent exit node. This can introduce new risks while solving others.’
“If the VPN/SSH server is adversary controlled you weaken the protection provided by Tor. If the server is trustworthy you can increase the anonymity and/or privacy (depending on set up) provided by Tor.”
User>VPN>Tor>Internet
Tor over VPN means you first connect to the VPN, before loading up Tor to access the website of your choice. It’s also known as ‘Onion over VPN’.
VPN encryption prevents the Tor entry node from seeing your IP address, which closes off one potential vulnerability while accessing .onion sites. In other words, you’ll never directly connect to Tor with your internet connection, as you’ll be using the VPN as a tunnel to access the browser.
As we’ve mentioned above, this is a potential vulnerability, especially if the server you’re connecting to is untrustworthy. Issues could appear in the form of being identified by the service or having your data sold on to interested parties.
Of course, a trustworthy, audited VPN service will be helpful in this regard. It will offer increased security compared to solely using the Tor browser. However, this does have an impact on speeds.
User>Tor>VPN>Internet
VPN over Tor involves connecting to Tor first, so the VPN IP will be used as an exit node. This allows for more privacy from a VPN provider, while your ISP will only be able to see that you’ve connected to Tor.
This means that users are limited by the slow speeds of the Tor network. So, it’s not recommended unless you don’t trust the VPN provider.
Both VPNs and Tor are great ways to provide online anonymity, although they’re different in many respects.
Tor is a browser that can be used to access restricted content, and the service is completely free of charge. This can lead to a notable slowdown, especially when there are lots of users hogging the service.
A VPN uses tunneling to keep the data sent to and from your device encrypted. This includes all traffic, including data transmitted outside of the browser. We’d advise you to stick with a premium VPN provider to ensure that you’ll have no issues relating to privacy.
Essentially, a VPN is helpful in terms of both privacy and anonymity, while Tor provides no encryption. The latter still helps to provide anonymity online, although it is much slower. They can also be used together, with Tor over VPN the preferred method to do so.
WHAT’S IN THIS REVIEW?
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cfduid | 1 month | The cookie is used by cdn services like CloudFlare to identify individual clients behind a shared IP address and apply security settings on a per-client basis. It does not correspond to any user ID in the web application and does not store any personally identifiable information. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Advertisement". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 1 year | This cookies is set by GDPR Cookie Consent WordPress Plugin. The cookie is used to remember the user consent for the cookies under the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-non-necessary | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Non-necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 1 year | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 1 year | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 1 year | No description |